The Primary Site for Reabsorption of Solutes and Water Is
Which of these cannot pass through the filtration membrane. Various portions of the nephron differ in their capacity to reabsorb water and specific solutes.

When The Kidneys Fail People With Kidney Failure 腎衰竭 Must Be Treated Immediately Ppt Download
27-11 Only 10 Na 20 H 2 O from original filtrate remaining Na reabsorption enhanced by aldosterone Site of atrial naturietic peptide activity Na reabsorption blood vol.

. Describe the reabsorption of water and solutes along the renal tubule. Secretion is important for removal of substances that arent filtered such as drugs and. Water moves from the tubular fluid into the cell in response to this gradient.
See full answer below. The osmotic and electrical gradients that drive the reabsorption of water and solutes is created by reabsorption of the solute ___________________. This control is exerted directly by ADH and aldosterone and indirectly by renin.
The primary site for reabsorption is the proximal convoluted tubule PCT. It is where all glucose most amino acids and the majority of salts are reabsorbed. The proximal convoluted tubule is the primary site for the reabsorption of solutes and water.
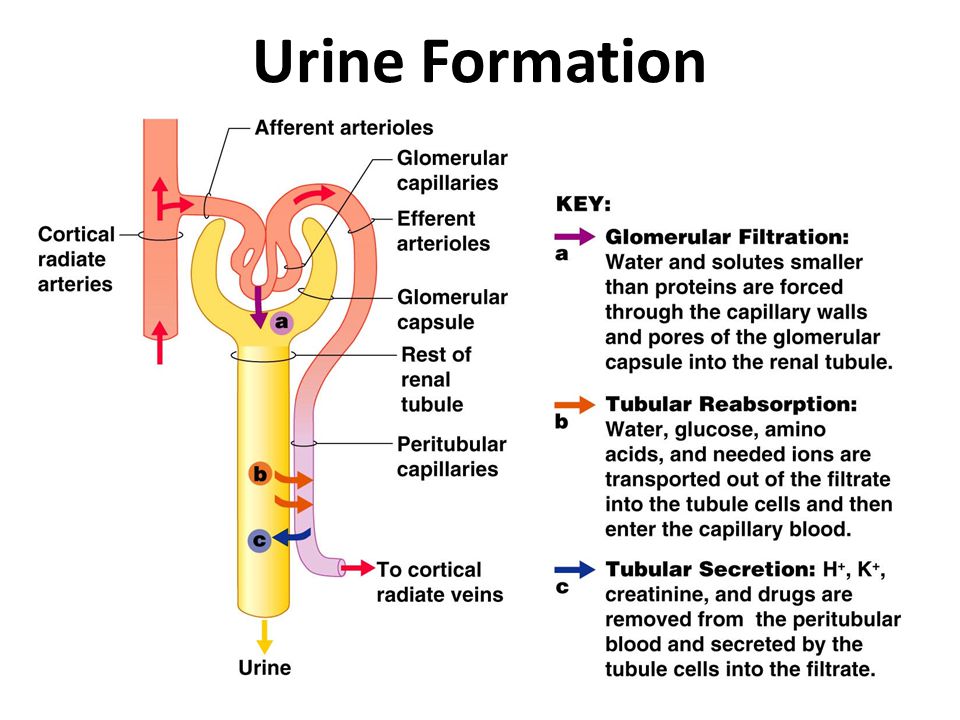
Notes Reabsorption Removes solutes and water from the tubular fluid and returns them to the blood. Refer to the accompanying figure. All of these substances were absorbed in the digestive tract99 percent of the water and most of the solutes filtered by the nephron must be reabsorbed.
Defects in their location andor expression along the renal tubule underlie many kidney diseases. Asked Nov 22 2020 in Anatomy Physiology by real2real. The distal convoluted tubule is the primary site for the reabsorption of solutes and water.
Secretion Moves solutes from the blood and nephron tubule cells into the tubular fluid. See the answer See the answer done loading. The loop of Henle.
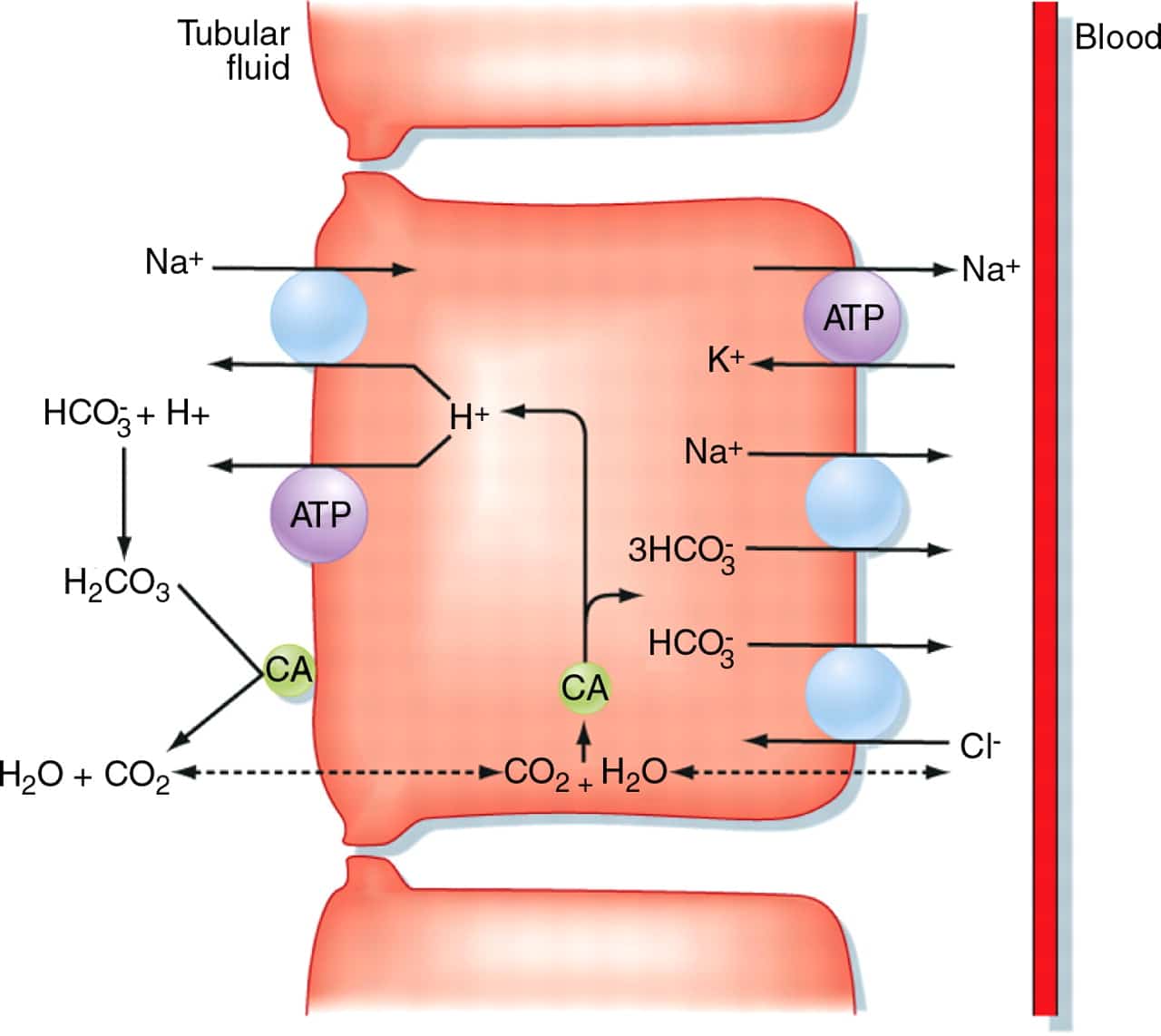
The proximal convoluted tubule is the primary site for the reabsorption of solutes and water. The net effect is water reabsorption from the tubular fluid into the peritubular capillaries caused by the increased oncotic pressure of the capillary blood and the active reabsorption of Na. The cuboidal cells of the proximal convoluted tubule have numerous microvilli and mito-chondria and they are well adapted to transport molecules and ions across the nephron wall by active transport and cotransport.
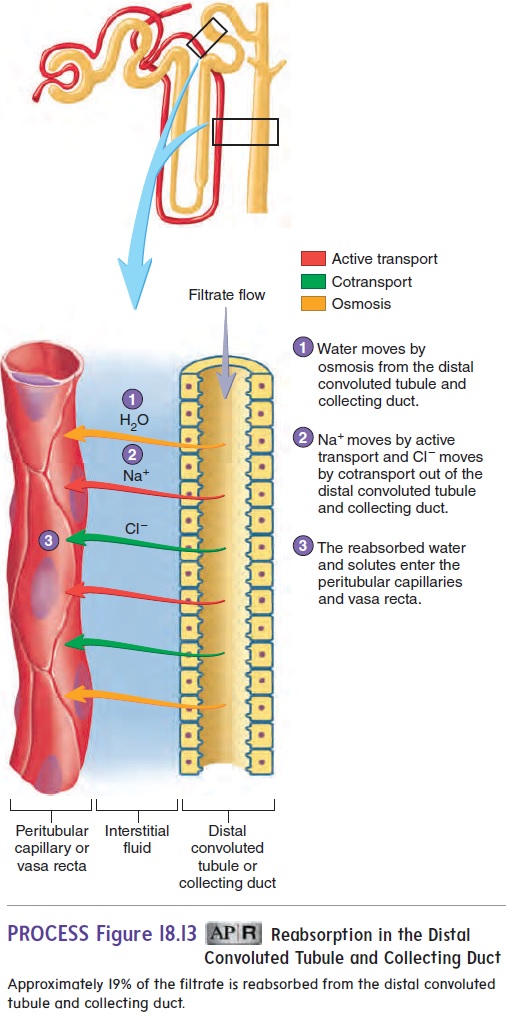
Fortunately tubular reabsorption mechanisms in the nephrons of your kidneys return the water and solutes that you need back into your extracellular fluid and circulatory system. This distal convoluted tubule is the primary site for the reabsorption of solutes and water. There are 3 main places where H 2 O reabsorption occurs.
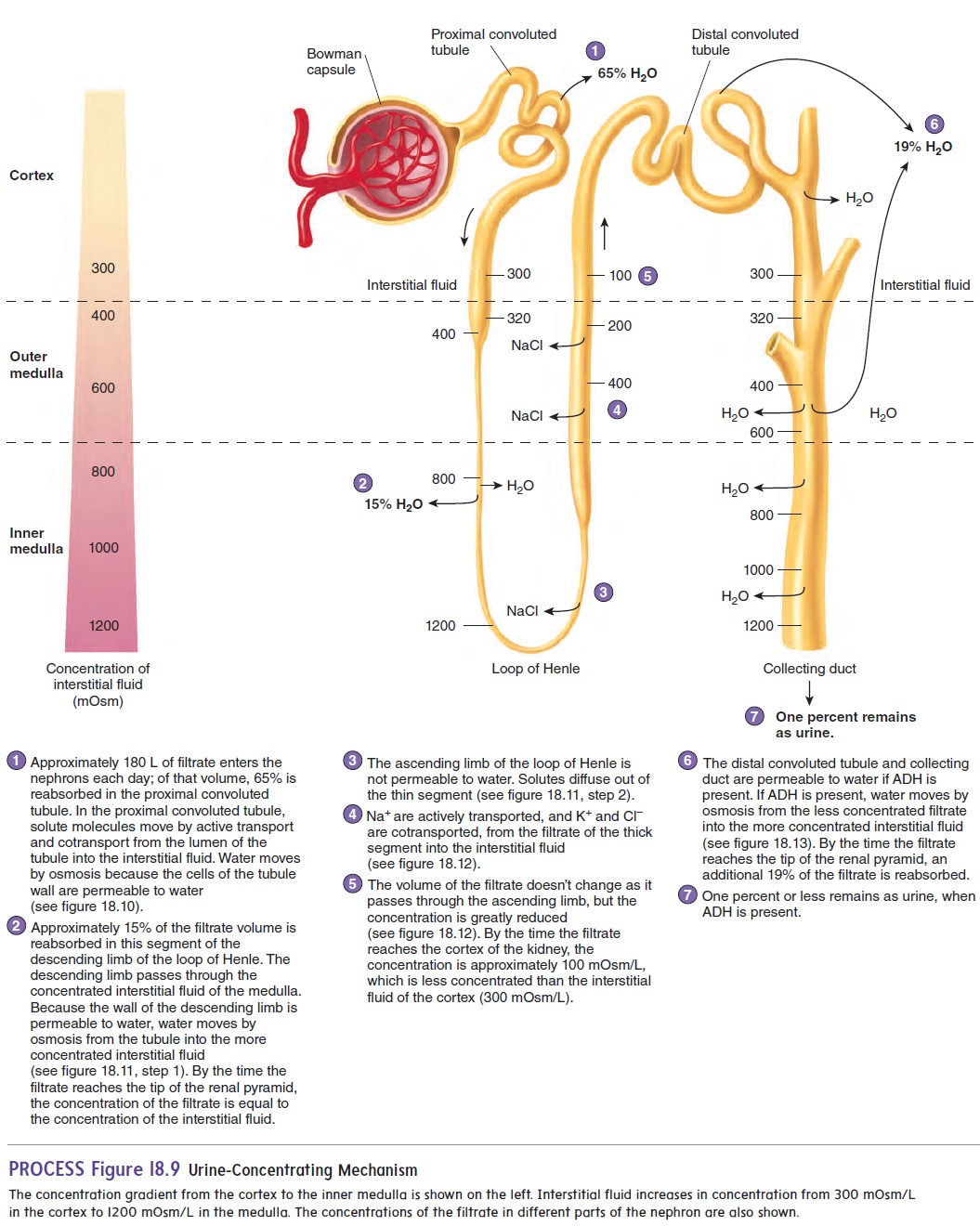
Reabsorption of solutes with nutritional value occurs at the point labeled as. The descending loop of Henle is permeable to water and will reabsorb water. It is also important to note that water reabsorption is heavily driven by the movement of Na as a rule of thumb water tends to follow the direction that sodium moves in.
The primary site for reabsorption of solutes of water is the loop of Henle. Additional reabsorption dependent on body needs Fig. Water and substances that are reabsorbed are returned to the circulation by the peritubular capillaries and vasa recta capillaries that surround the nephron tubules.
It reclaims much of the water ions and nearly all of the nutrients that are filtered. Aldosterone acts on the collecting tubule and duct cells to increase Na. Specific transporter proteins are inserted into these distinct cell membranes which mediate reabsorption and secretion of solutes and water.
Water and substances that are reabsorbed are returned to the circulation by the peritubular and vasa recta capillaries. The primary site for reabsorption of solutes and water is A. The proximal convoluted tubule is the primary site of absorption.
In addition 65 of filtered Na is reabsorbed. While much of the reabsorption and secretion occur passively based on concentration gradients the amount of water that is reabsorbed or lost is tightly regulated. A regulation of blood volume b excretion of wastes c regulation of erythrocyte production d regulation of lymphocyte production 3.
Some water is also reabsorbed across the tight junctions. The cuboidal cells of the proximal convoluted tubule have numerous microvilli and mito-chondria and they are well adapted to transport molecules and ions across the nephron wall by active transport and cotransport. Because the apical and basolateral membranes of proximal tubule cells express aquaporin water channels water is primarily reabsorbed across the proximal tubular cells.
Regulation of water and electrolyte balances. All of these substances were absorbed in the digestive tract99 percent of the water and most of the solutes filtered by the nephron must be reabsorbed. Water reabsorption is coupled with the reabsorption of solutes in the proximal convoluted tubule in.
A hormone is a substance that is secreted from an endocrine gland or gonad and transported through the blood to the site of action. REABSORPTION OF SOLUTES WATER The primary site for reabsorption is the proximal convoluted tubule PCT In the initial 23 of the PCT 100 of filtered glucose and amino acids and 80 of filtered bicarbonate HCO3 - are reabsorbed. In addition to reabsorbing the substances that you need your nephrons are able to secrete unwanted substances from your bloodstream into the filtrate.
Hormones control tubular reabsorption to regulate body fluid volumes and solute concentrations. The proximal convoluted tubule PCT the descending limb of the Loop of Henle and the collecting ducts.

Water Absorption An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Urine Formation Tubular Reabsorption Is Selective And Quantitatively
The Proximal Convoluted Tubule Channels Teachmephysiology
Which Part Of The Nephron Is Responsible For The Maximum Reabsorption Of Water Quora
Tubular Reabsorption Urine Production

The Urinary System Physiology Nursing School Studying Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Tubular Reabsorption Formation Of Urine Urinary System
Physiology Of Urine Formation Online Biology Notes

Water Absorption An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Tubular Reabsorption Urine Production
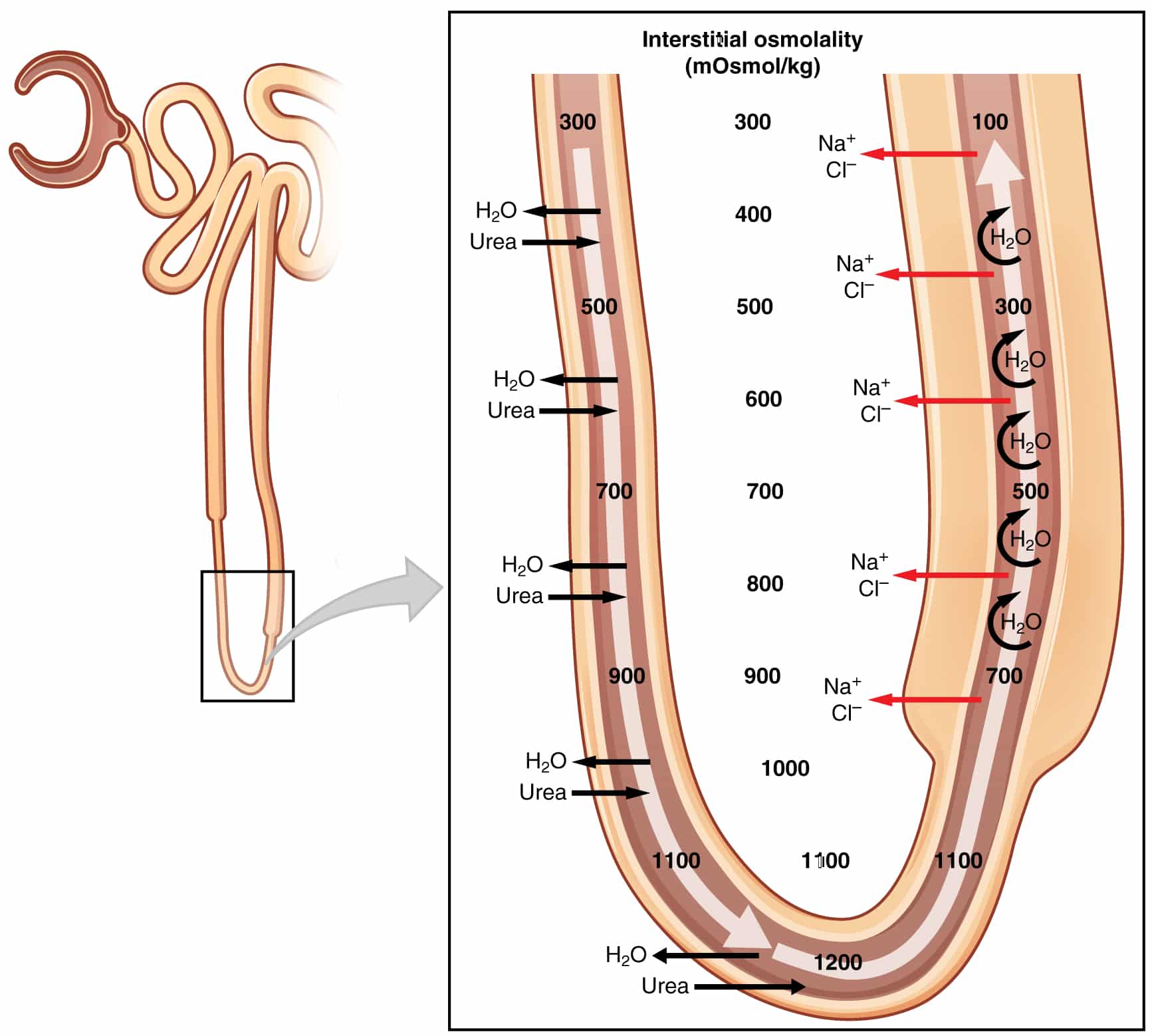
The Loop Of Henle Function Diuretics Teachmephysiology

Routes And Mechanisms Of Tubular Reabsorption And Secretion Flashcards Quizlet

Reabsorption Capabilities Of Different Segments Of The Renal Tubules And Collecting Ducts Renal Physiology Nursing School Studying Anatomy And Physiology

Tubular Reabsorption Anatomy And Physiology Ii
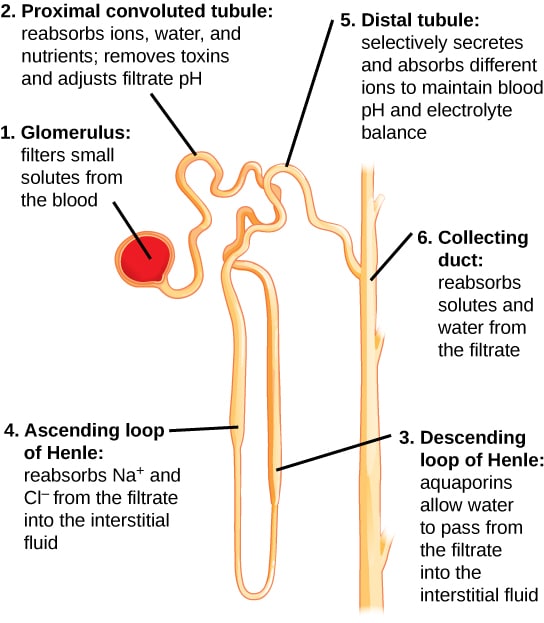
Water Filtration And Reabsorption Urinary Teachmephysiology

Pin By Yasin On Physiology Excretion And Osmoregulation Body Fluid Body Protein Organic Nutrients
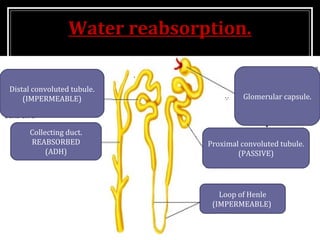

Comments
Post a Comment